Using Morphology to Teach Vocabulary
The importance of improving students’ vocabulary cannot be overstated. Having a large vocabulary helps students to develop their reading comprehension and writing skills. In fact, research has shown that children with larger vocabularies achieve better results at school, including higher reading achievement in particular.
Targeting morphology is one way to teach vocabulary.
What is morphology?
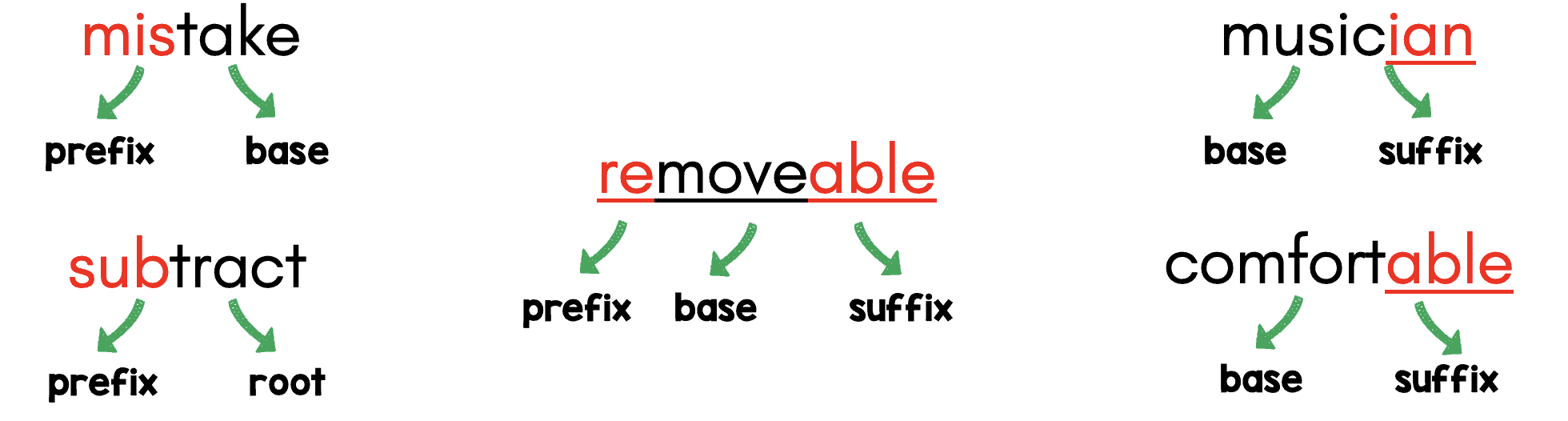
Morphology is the study of words and their parts. Morphemes, like prefixes, suffixes and base words, are defined as the smallest meaningful units of meaning. Morphemes are an important part of phonics in both reading and spelling, as well as for vocabulary and comprehension development.
Why teach morphology?
Teaching morphemes unlocks the structures and meanings within words. If students have a strong understanding of prefixes, suffixes and base words, they can use this knowledge to decode the meaning of new words. For example, if a student knows that ‘-less’ means ‘without’, then they can use that knowledge to define the word ‘careless’ (without care).
- build word sense.
- build literacy skills.
- build knowledge in content.
- build an understanding of multiple meanings, through the study of word families. (Shanahan, 2020).
Teaching morphology helps students:
- gain strategies for decoding new words when reading.
- understanding spelling patterns that exist in English words.
- enhance their vocabulary which improves the quality of writing.
Here is what experts and researchers also have to say:
- Learning to recognise morphemes helps students to decode complex words more rapidly, to learn the meaning of words, and to spell them correctly (Such, 2021).
- A meta-analysis conducted by Bowers et al (2010) of 22 morphology studies found that morphology instruction benefits learners, especially less proficient readers.
- Carlisle (2010) analysed 16 studies about how morphological awareness contributes to students’ literacy development. The findings showed that morphological awareness has the potential to deepen students’ understanding of spelling and the meaning of written words.
- When students encounter new or unfamiliar words in a text, they can use their understanding of prefixes, suffixes and base words to decode the meaning of the whole word (Apel & Henbest, 2016).
- Morphological awareness is another tool in a student’s literacy knowledge tool-belt when they encounter new and challenging words (Goodwin, Lipsky, & Ahn, 2012).
Where morphology fits within the reading rope

This image originally appeared in the following publication: Scarborough, H. S. (2001). Connecting early language and literacy to later reading (dis)abilities: Evidence, theory, and practice. In S. Neuman & D. Dickinson (Eds.), Handbook for research in early literacy (pp. 97–110). New York, NY: Guilford Press.
The Reading Rope (Scarborough (2001) shows the skills students need to become skilled readers. One of the key skills students need is vocabulary. As this blog post has been explaining, teaching morphology is one way to grow vocabulary.
In addition, the Reading Rope acknowledges background knowledge as an essential contributor to skilled reading. Understanding morphology concepts builds students’ background knowledge that they can bring to new and more complex texts.
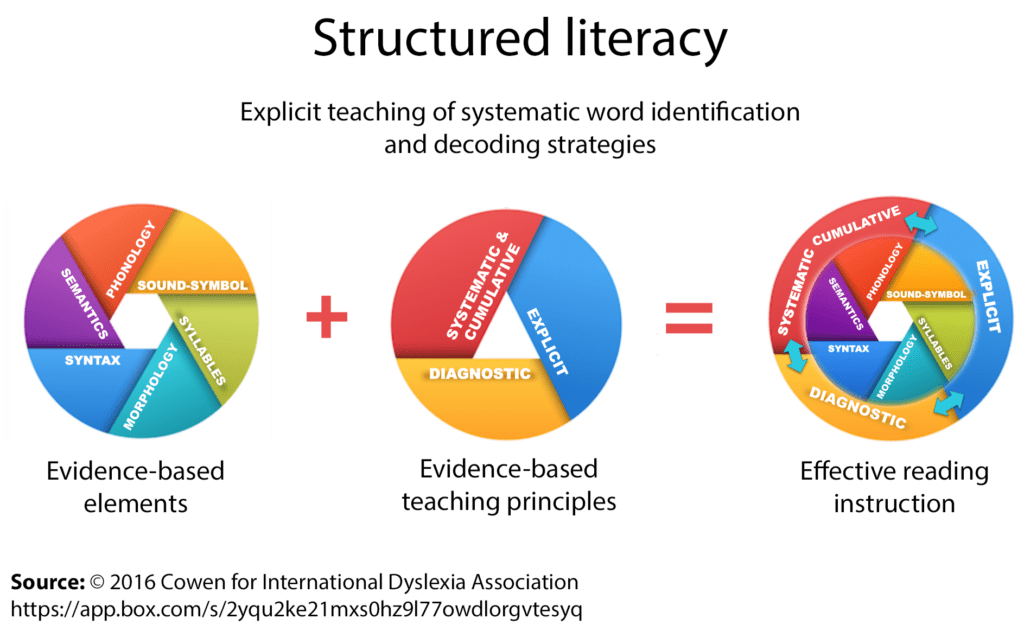
Where morphology fits within structured literacy
Morphology is one of the six evidence-based components of structured literacy.
Four Ways to Teach Morphology
Your students can become word detectives! Encourage a problem-solving approach to word study: constructing and deconstructing words, and exploring how their origins impact their meaning.
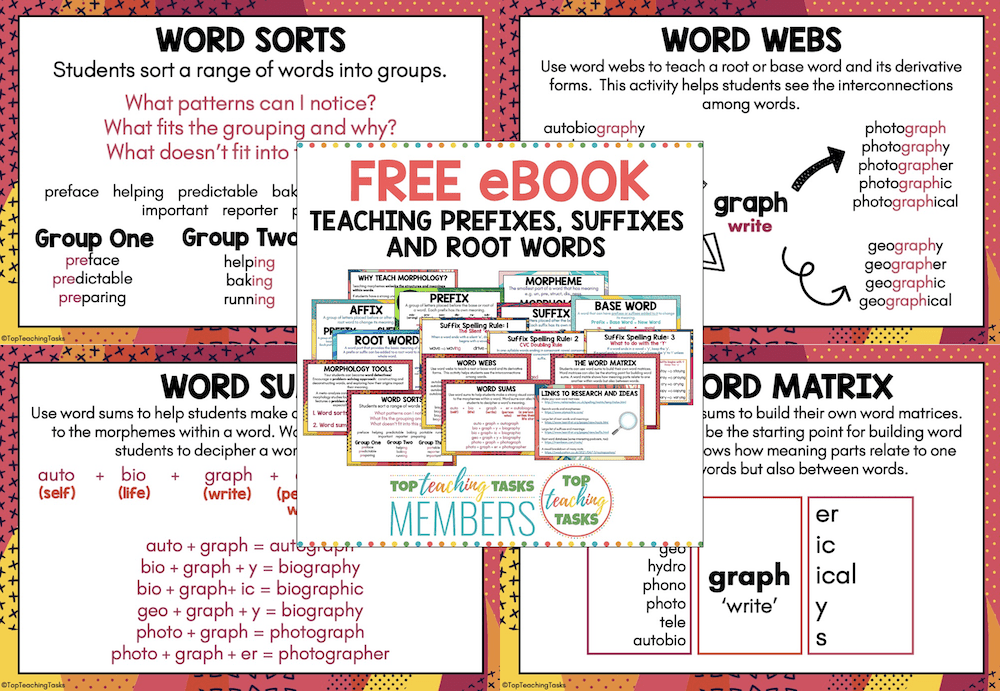
1. Word Sorts: Students sort a range of words into groups.
What patterns can I notice? What fits the grouping and why?What doesn’t fit into this group?
2. Word Webs:
Use word webs to teach a root or base word and its derivative forms. This activity helps students see the interconnections among words.
3. Word Sums:
Use word sums to help students make a strong visual connection to the morphemes within a word. Word sums can also help students to decipher a word’s meaning.
4. Word Matrices
Students can use word sums to build their own word matrices. Word matrices can also be the starting point for building word sums. A word matrix shows how meaning parts relate to one another within words but also between words.
If you would like more information about these four ways of teaching morphology, keep reading to sign up for our free eBook.
Our Morphology Resources
We have a growing range of morphology resources to compliment your vocabulary teaching program. See more here.
Did you say freebie?
We’ve put together a free 15-page eBook full of definition posters, spelling rules, morphology teaching tools, and links to research and ideas. Get your free eBook here.
Have You Joined Top Teaching Tasks Members?
The best way to access ALL of our resources is with a Top Teaching Tasks Membership. Learn more here.